60 years of space innovations
In 1964, the TNO's voyage into space began with the launch of its first space instrument, the S59 spectrometer. Fast forward to 2024, we commemorate the 60th anniversary of TNO's pioneering achievements in space instrumentation. From the archives, we bring you the milestones of space instrumentation that showcase a legacy of technological innovation.
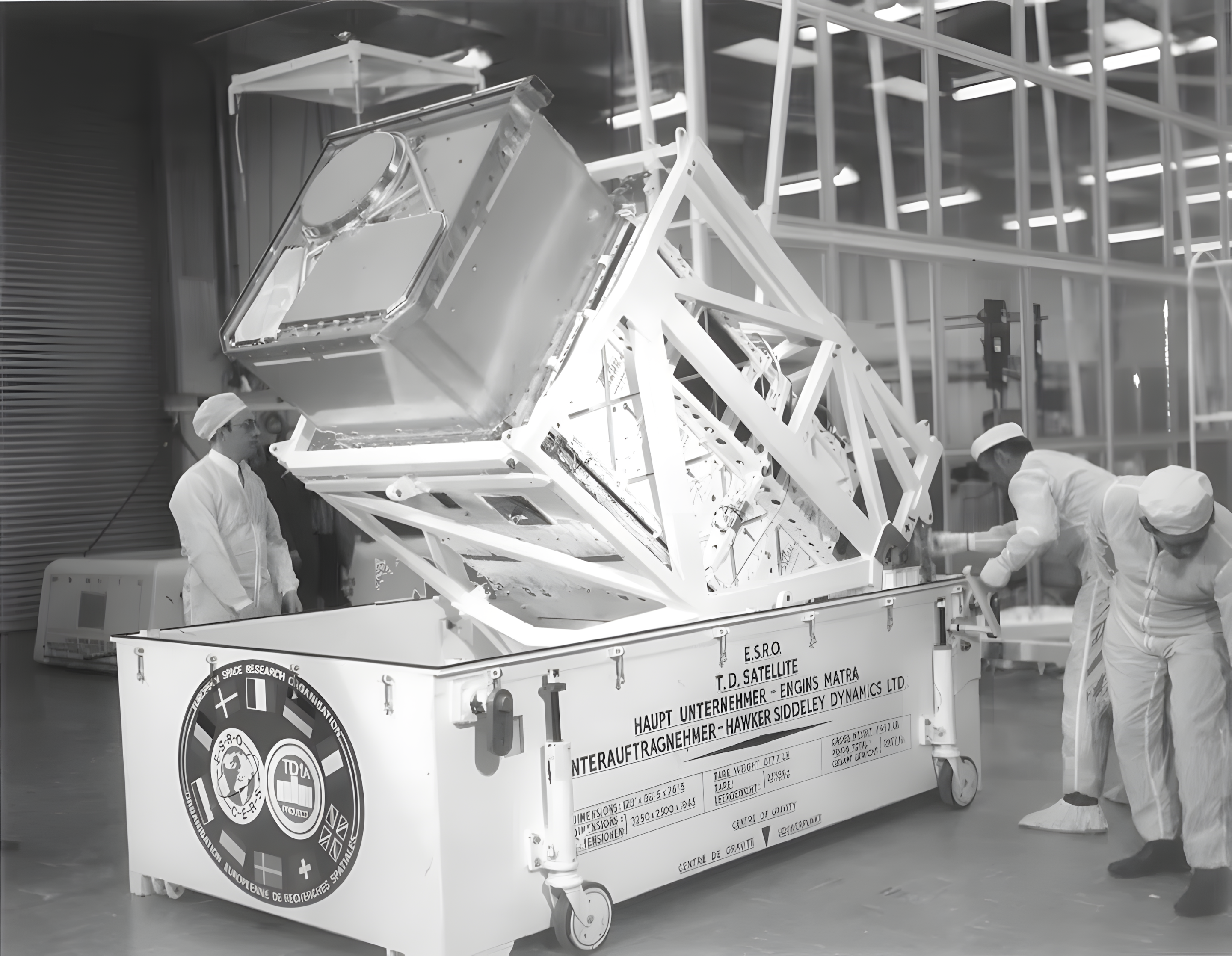
S59 spectrophotometer
To start with the S59 spectrophotometer. Which was a significant technological breakthrough of its time, was meticulously crafted to function in the near-UV spectrum (206-287 nm), delivering exceptional precision with a resolution of 0.18 nm. This instrument's deployment aboard the TD-1A satellite marked a critical advancement in the field, achieved in collaboration with the European Space Research Organisation.
Time setters in Space
Our time setters are the driven professionals who push boundaries every day. They develop innovative solutions in this case regarding space innovations.
"Proud to be working on something that is orbiting around the world" - Latica Pletikapić Exle | Project Manager TNO Optics
Latica is developing compact optical terminals that can be placed in small satellites - such as TNO’s CubeCAT, a powerful 10x10x10 cm terminal that enables bi-directional space-to-ground communication links between the satellite and an optical ground station. But our CubeCAT terminal alone is not enough.
"My job requires going back and forth between fundamental insights and thinking in applications with high technology readiness level. It challenges me." - Gustavo Castro do Amaral | Senior scientist TNO Quantum Technology
Space acts as a vast and innovative platform for Gustavo to leverage in advancing quantum internet technologies. It enables the integration of satellite communications with quantum computing, facilitating the transfer of information across unprecedented distances.




