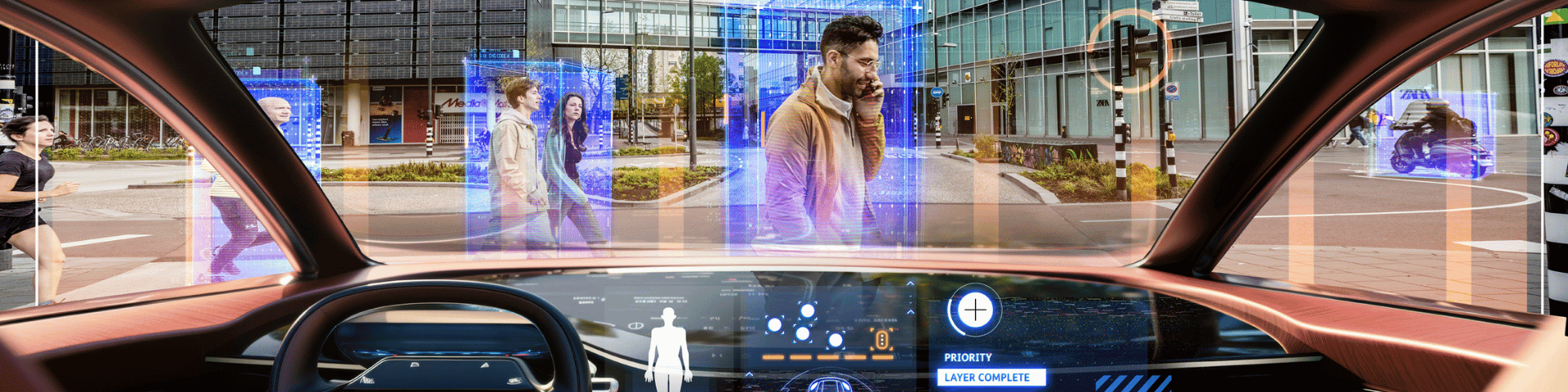
Safe AV-human interaction
People play an integral role in the context of automated driving and present unique challenges that require specific attention. While many safety considerations in automated driving focus on engineering aspects and address hardware and software failures that could lead to collisions, understanding human behaviour and interaction with automated vehicles (AV’s) is equally crucial.
Current challenges automated vehicles
Understanding and modelling human behaviour is crucial for predicting and assessing the safety of interactions between people and automated vehicles, both inside and outside the vehicle. In the context of co-drivership, the technology should be capable of estimating the driver's state. Additionally, in traffic situations, the vehicle needs to be able to understand and appropriately respond to other road users and pedestrians.
One of the significant challenges is the diversity of regulations and their interpretation; the definition of a 'competent and attentive driver' for example, allows for considerable room for interpretation.
A potential threat to the success of automated driving is motion sickness. In a self-driving car where drivers become passengers, motion sickness can greatly impact the overall comfort and usability of the vehicle. Furthermore, the expectation of passengers being able to engage in other activities during travel may be compromised.
Our vision on safe automated driving
For TNO safe automated driving is about more than avoiding accidents. Embracing a responsible and socially aware driving style significantly enhances safety. Since driving is a social activity influenced by technology, self-driving vehicles should adopt a driving demeanour that is acceptable to human road users.
Even with automation, humans remain partially engaged in driving, necessitating safe transitions of control. Drivers should comprehend the vehicle's capabilities, while the vehicle should also understand the driver's abilities.
To effectively address motion sickness with automated driving, we must understand the fundamentals so we can design vehicles that help prevent it.
TNO’s development of scientifically grounded methodologies for safety assessments provides a robust framework for evaluating automated driving technologies by vehicle manufacturers and for approval by regulatory authorities. Our holistic approach to safe automated driving draws upon our expertise in traffic dynamics, behavioural psychology, human physiology, and data science.
Our solutions
The variability in driver involvement with current Driver Control Assistance Systems (DCAS) and Level 3 Automated Lane Keeping Systems (ALKS) poses a significant challenge for the industry. Drivers must be prepared to take over the wheel at any moment, necessitating a thorough understanding of driver situational awareness and mental engagement.
Current legislation regarding Driver Control Assistance Systems (DCAS) may inadvertently foster misplaced trust in automated driving systems' situational awareness. While regulations focus on physical and visual engagement (e.g., 'eyes on the road, hands on the wheel'), mental engagement of the driver is equally critical. Ensuring that drivers are mentally engaged and capable of taking control promptly when needed is essential for safe automated driving.
At TNO, we are dedicated to developing innovative methodologies for assessing driver awareness. By monitoring and analysing driver behaviour and awareness in specific driving situations, we aim to determine the driver's readiness for a safe transition of control. Through these efforts, we seek to establish a comprehensive model that assesses driver awareness, including mental engagement, to enhance the safety of automated driving systems.
To conduct this research, TNO leverages its expertise in automated vehicle technology, understanding its weaknesses, and combines this with knowledge of behavioural psychology. Additionally, TNO offers unique research facilities, including driving simulators and driver monitoring equipment, to investigate and advance methods for assessing driver awareness and readiness in automated driving scenarios. This interdisciplinary approach allows TNO to develop effective solutions that enhance the safety of automated driving.
Vehicle safety is not just about accident statistics, but also about perceived safety and a safe driving style. For a smooth adoption of automated driving it is essential to establish trust with other road users.
The recently introduced European regulations for automated driving systems, such as Automated Lane Keeping Systems (ALKS) and Driver Control Assistance Systems (DCAS), contain abstract guidelines that allow for various interpretations. These regulations require automated systems to exhibit 'responsible, predictable, and conflict-avoiding behaviour' and should be capable of handling 'foreseeable events'.
The challenge for the industry and authorities is to translate these subjective guidelines, which are difficult to assess, into objective engineering requirements and specific automated driving characteristics. Clear guidelines for the industry and authorities help build confidence in the reliability and performance of automated systems.
With StreetProof, TNO offers a unique solution by developing technical requirements to achieve this Safe & Social driving style. As opposed to our scenario based safety assessment programme, aimed at detecting and preventing unsafe behaviour, this innovation programme focuses on adopting driving behaviour that contributes to road safety. We have succeeded in translating formal and informal guidelines for driving behaviour into mathematical formulas, allowing us to create behavioural models from various sources of real-world driving data. These models are then converted into technical specifications. Subsequently, we use human evaluation to assess whether this driving behaviour is acceptable or not.
The advancement of automated driving has significantly raised awareness in the automotive industry regarding motion sickness. With drivers transitioning to passengers in self-driving cars, there is a heightened susceptibility to motion sickness among occupants. This shift has prompted increased focus on addressing motion sickness as a critical consideration in the development of automated vehicles.
Motion sickness has been a longstanding issue associated with car travel, affecting passengers more frequently than drivers. Studies suggest that up to 62% of passengers experience motion sickness, compared to about 24% of drivers. In self-driving vehicles, more individuals are likely to encounter motion sickness. Addressing this issue is crucial for the successful adoption of automated driving technologies. Without targeted interventions, motion sickness could pose significant challenges to the widespread acceptance of autonomous vehicles.
TNO has extensive expertise in researching motion sickness and collaborates closely with industry partners to develop effective solutions for addressing this issue in the development of self-driving vehicles. Car manufacturers are leveraging TNO's models to predict motion sickness, allowing considerations of well-being and comfort in programming the driving behaviour of autonomous vehicles. Safety is also a critical aspect, ensuring that drivers are capable of taking over the driving task when needed.
In addition to physical motion sickness, TNO also specialises in cybersickness, which is relevant given the expected increase in virtual reality (VR) applications in cars due to automated driving. The combination of physical and virtual motion sickness presents new challenges and TNO's expertise is instrumental in navigating this emerging area.
The expertise and facilities at TNO to research driving comfort and motion sickness are unparalleled globally. With a multidisciplinary team of human factors experts and state-of-the-art facilities, including a one-of-a-kind three-dimensional motion simulator, TNO possesses unique capabilities for research and development in the field of human factors and motion simulation.
Get inspired
How is YER award winner Chris van der Ploeg doing?


TNO launches Motion Comfort Institute for automated vehicle era


Releasing autonomous software faster with DeepScenario and TNO’s StreetWise
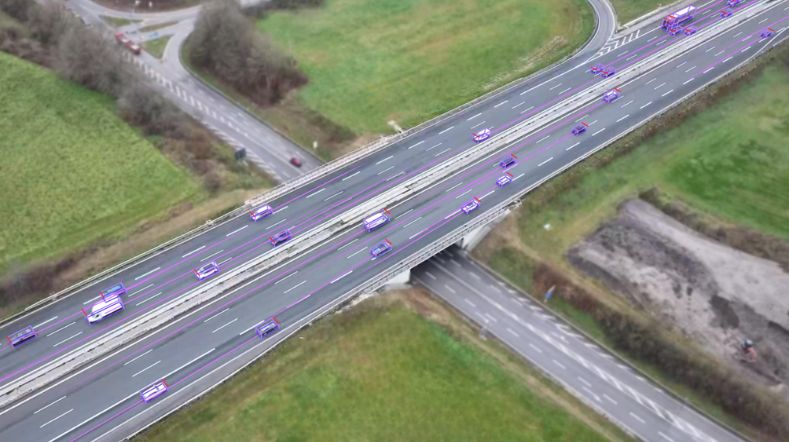


MARQ opens its doors: a place to collaborate on the mobility of the future

Demonstrations of automated driving and charging for logistics at Maasvlakte


