D8 Advance X-Ray Diffraction
- Category:
- Measure
- Brand:
- Bruker
- Type:
- D8
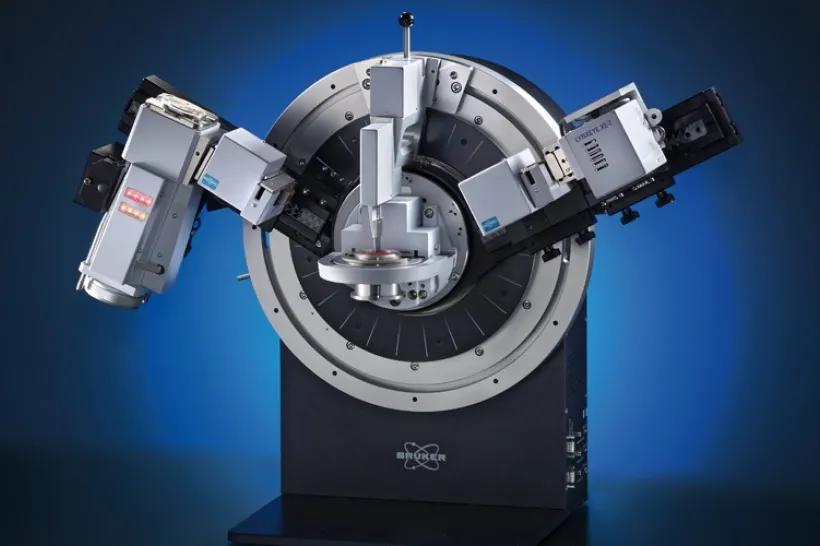

Description
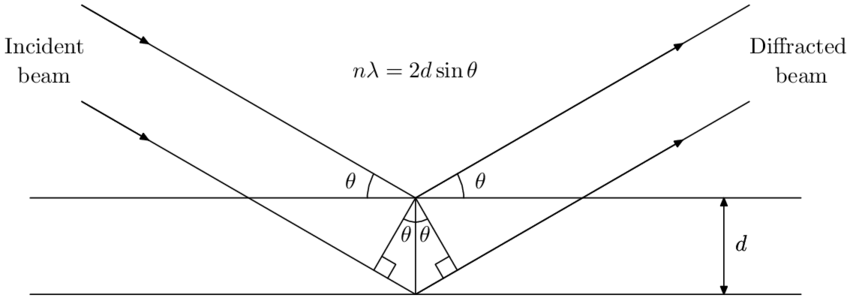
X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a technique in which the diffraction of X-rays by a sample of interest is analyzed. When used as a basic technique (X-ray powder diffraction), it can determine the crystalline components of a sample. Taking it a step further, it can also provide information on the mass percentages of the crystalline components and the amount of amorphous material.
The technique can be further applied to a wide range of applications, including but not limited to various scattering techniques and reflectometry.
Technical details
The D8 Advance diffractometer accommodates a range of sample types with minimal preparation, particularly for powders which can be loaded directly. Thin films might require mounting on substrates, while bulk materials can be analyzed as-is.
The system features a high-resolution goniometer, ensuring precise measurement of diffraction angles. The ceramic X-ray tube provides a stable and intense X-ray beam, crucial for obtaining high-quality diffraction patterns.
Our D8 advance supports various stages, including a capillary stage, XYZ stage and a humidity and temperature stage which is particularly useful for in-situ experiments.
Additional techniques
Powder X-ray diffraction is often used in combination with other analytical techniques that can provide information about the composition of the sample. Chemical bulk data obtained with XRF or ICP-MS complement the knowledge gained from X-ray diffraction to determine the specific composition of a material. Techniques such as scanning electron microscopy, particle size determination using laser diffraction, or thermal analysis can also be applied to similar samples to enhance understanding.
Applications
The D8 Advance diffractometer has various applications, including:
- Phase Identification: determining different phases within a sample.
- Crystallite Size Determination: measuring the size of coherent diffraction domains.
- Quantitative Analysis: assessing the relative amounts of different phases in multi-phase samples.
- Structural Analysis: investigating the crystal structure of materials.
- In-situ Experiments: analyzing material behavior under varying temperature and humidity conditions.